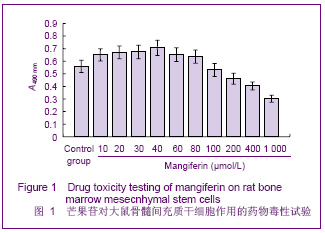
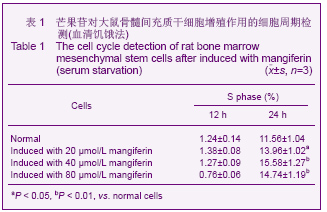
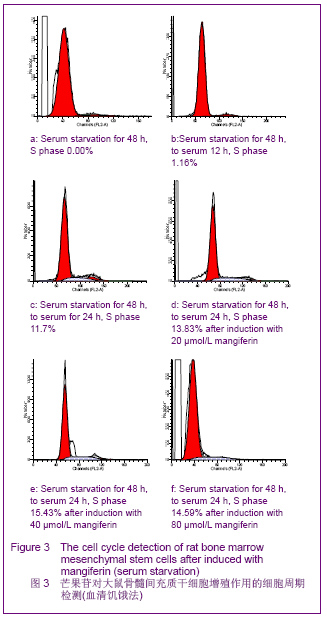
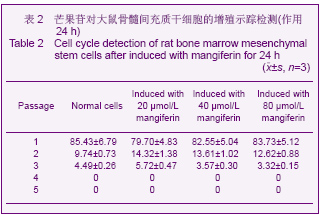
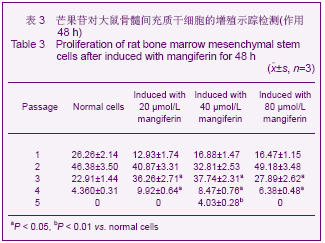
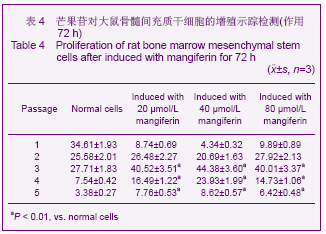
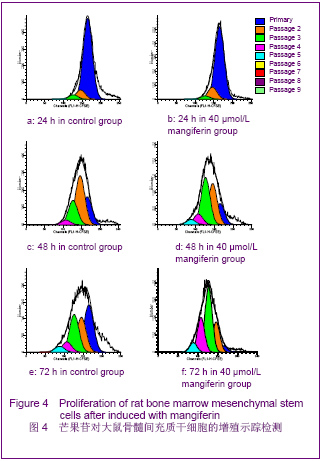
| [1] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999;284 (5411):143-147.[2] Li XF, Zhao JM, Su W, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(10): 1721-1725.李晓峰,赵劲民,苏伟,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(10):1721-1725.[3] Friedenstein AJ, Piatetzky S II, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol 1966;16(3):381-390.[4] Campagnoli C, Roberts IA, Kumar S, et al. Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow. Blood. 2001;98(8): 2396-2402.[5] O’Donoghue K, Choolani M, Chan J,et al. Identification of fetal mesenchymal stem cells in maternal blood: implications for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis. Mol Hum Reprod. 2003; 9(8):497-502.[6] Lee OK, Kuo TK, Chen WM,et al. Isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Blood. 2004;103(5):1669-1675.[7] Agarwala S, B NR, Mudholkar K, et al. Mangiferin, a dietary xanthone protects against mercuryinducedtoxicity in HepG2 cells. Environ Toxicol. 2012;27(2):117-127.[8] Yoosook C, Bunyapraphatsara N, Boonyakiat Y,et al. Anti-herpes simplex virus activities of crude water extracts of Thai medicinal plants.Phytomedicine. 2000;6(6):411- 419. [9] Campos-Esparza MR, Sánchez-Gómez MV, Matute C. Molecular mechanisms of neuroprotection by two natural antioxidant polyphenols.Cell Calcium. 2009;45(4):358-368. [10] Garrido-Suárez BB, Garrido G, Delgado R, et al. A Mangifera indica L. extract could be used to treat neuropathic pain and implication of mangiferin.Molecules. 2010;15(12):9035-9045.[11] Rajendran P, Ekambaram G, Sakthisekaran D. Cytoprotective effect of mangiferin on benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung carcinogenesis in swiss albino mice.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;103(2):137-142. [12] Lin H, Chen R, Liu X, et al. Study on interaction of mangiferin to insulin and glucagon in ternary system.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2010;75(5):1584-1591.[13] Prabhu S, Jainu M, Sabitha KE,et al. Cardioprotective effect of mangiferin on isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in rats.Indian Journal Of Experimental Biology .2006;44(3): 209-215.[14] Muruganandan S, Srinivasa K, Gupta S, et al. Effect of mangiferin on hyperglycemia and atherogenicity in streptozotocin diabetic rats.Journal Of Ethnopharmacology. 2005;97(3): 497-501.[15] Pardo Andreu GL, Maurmann N, Reolon GK, et al. Mangiferin, a naturally occurring glucoxilxanthone improves long-term object recognition memory in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010; 635(1-3):124-128.[16] Aggarwal BB. Nuclear factor-kappaB: the enemy within. Cancer Cell 2004;6:203–208.[17] Huang H, Zhao N, Xu X, et al. Dose-specific effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Prolif. 2011;44(5):420-427.[18] Kushner JA, Ciemerych MA, Sicinska E, et al. Cyclins D2 and D1 are essential for postnatal pancreatic beta-cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(9):3752-3762.[19] Campbell KJ, Rocha S, Perkins ND. Active repression of antiapoptotic gene expression by RelA(p65) NF-kappa B.Mol Cell. 2004;13(6):853-865.[20] Fu M, Wang C, Li Z, et al. Minireview: Cyclin D1: normal and abnormal functions. Endocrinology. 2004;145(12):5439-5447.[21] Wang DX,Jiang HX,Su SB,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2010;14(10):1764-1768.王东旭,姜海行,苏思标,等.体外共培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞对肝星状细胞增殖的影响:Cyclin D1与P27表达调控[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(10):1764-1768. [22] Tomita N. BCL2 and MYC dual-hit lymphoma/leukemia.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011;51(1):7-12. [23] Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood .1992;80(4):879-886. |